Clouds of barium ions
An atom can become ionized by the absorption of light. The atom of barium is particularly easy to ionize, because its outermost electron is very loosely bound. If a mass of barium is vaporized in space, producing a barium cloud, much of the barium becomes ionized by sunlight within less than a minute. The cloud then moves in response to electric forces in space, and can be used to study the electrical field in space.

In practice the barium is packed into canisters with copper oxide, and these are released from rockets or satellites and ignited. The resulting chemical reaction produces great heat, but more barium is packed into the canister than can combine chemically, and some the excess is vaporized to form a large
spherical greenish cloud.
 Typically the release is done after sunset or before sunrise, so that while the canisters explode in full sunlight, observers on the ground can watch the cloud against the dark sky: soon a bluish ion cloud separates from the green one, usually elongated or striped in the direction of the magnetic field lines, which guide the ions.
Typically the release is done after sunset or before sunrise, so that while the canisters explode in full sunlight, observers on the ground can watch the cloud against the dark sky: soon a bluish ion cloud separates from the green one, usually elongated or striped in the direction of the magnetic field lines, which guide the ions.
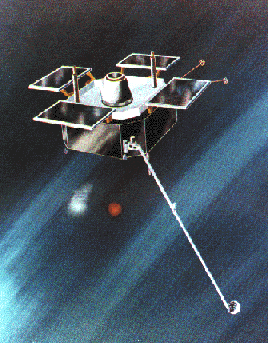
The AMPTE Charge Composition
Explorer (CCE) satellite
Some barium releases are conducted far from Earth and are tracked by telescopes. The AMPTE mission (Active Magnetospheric Particle Tracer Experiment), launched in 1984, released barium clouds near the "nose" of the magnetosphere and in the magnetospheric tail.
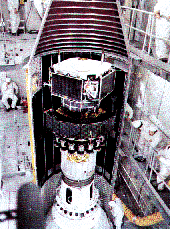
The AMPTE mission included three spacecraft, shown here stacked up during launch. Click here for a full size version of this image.
In addition it released a barium cloud in the solar wind to produce an "artificial comet". Soon after the cloud formed, the magnetic field embedded in the solar wind picked it and made it share the wind's flow, a process similar to the one which creates the ion tails of comets (see solar wind, history).
Questions from Users:
***
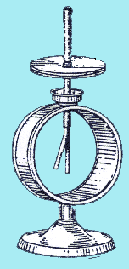 This leakage was used, around 1900, to detect radioactive emissions and measure their intensity. The drawing below shows a simple instrument for performing such measurements. It is called an electroscope and contains two parallel leaves
of metal foil, protected from wind inside a metal box with transparent windows and attached to a metal rod insulated from the box and leading outside (drawing).
This leakage was used, around 1900, to detect radioactive emissions and measure their intensity. The drawing below shows a simple instrument for performing such measurements. It is called an electroscope and contains two parallel leaves
of metal foil, protected from wind inside a metal box with transparent windows and attached to a metal rod insulated from the box and leading outside (drawing).
 Typically the release is done after sunset or before sunrise, so that while the canisters explode in full sunlight, observers on the ground can watch the cloud against the dark sky: soon a bluish ion cloud separates from the green one, usually elongated or striped in the direction of the magnetic field lines, which guide the ions.
Typically the release is done after sunset or before sunrise, so that while the canisters explode in full sunlight, observers on the ground can watch the cloud against the dark sky: soon a bluish ion cloud separates from the green one, usually elongated or striped in the direction of the magnetic field lines, which guide the ions.
