|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(M-12) Trigonometry Proficiency Drill
|
Sections (M 6-11) gave you some principles of trigonometry. This section can provide you with practice in applying them. In some cases solutions are given, but do not peek at them until you have made a determined effort to solve them on your own
|
|
We have tried to avoid repetitive excercises: each set is different. Do them all--do not leave any out! It is assumed that you have available a calculator which can derive sines and cosines, and also has functions sin-1 and cos-1 which given sinA or cosA can find the angle A, in the range 0 to 180 degrees.
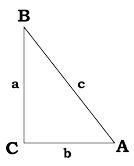 A triangle ABC has a right angle C and two sharp (or "acute") angles A and B. The triangle's sides AC and BC on both sides of the right angle C are given as: A triangle ABC has a right angle C and two sharp (or "acute") angles A and B. The triangle's sides AC and BC on both sides of the right angle C are given as:
(b) AC = 5 BC = 12 (c) AC = 8 BC = 15 In each case, use the theorem of Pythagoras to find the third side and then find the sine and cosine of angles A and B.
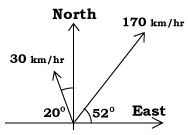
(The solution below uses vector components, as derived the section on vectors: read it only after you have tried to work out the problem yourself. Teachers in class may substitute different numbers and directions) Let us denote the velocity vector of the airplane relative to the air as V, that of the wind relative to the ground as W, and the velocity of the airplane relative to the ground U=V+W, where the addition is one of vectors. Draw a diagram with the given speeds and angles labeled appropriately. To perform the actual addition each vector must be resolved into its components. We get
Add:
|
|
|
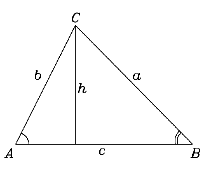
The problem: In the triangle ABC, the line AB is along a straight riverbank. We measure the distance c = AB as 118 meters, and angles A and B are 63° and 55° . What is the distance b = AC? Don't read any further until you have tried to solve it. Teachers in class may substitute different numbers and directions.
|
|
Because the sum of all angles is 180 degrees, the angle C must equal 62°. Then by the law of sines Multiply both sides by sin(55) to obtain the length b = AC. Further question: what is the perpendicular distance from C to the line c = AB? (hint: it equals the height h in the derivation of problem (4).)
|
|
|
If this formula somehow fails, the beam cannot leave the glass but is reflected from the boundary surface back into the glass, as from a mirror ("total internal reflection") The problem:Given B = 0, 20, 90, 60, 80 --what are the angles A? Does any of these beams fail to leave the glass?
|
|
Final trig section: The Tangent
Author and Curator: Dr. David P. Stern
Mail to Dr.Stern: stargaze("at" symbol)phy6.org .
Last updated 25 November 2001